Awabakal language facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Awabakal |
|
|---|---|
| Hunter River – Lake Macquarie | |
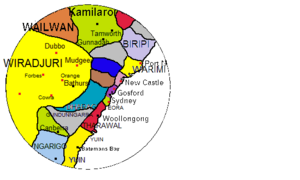
| Native to | Eastern New South Wales, Australia |
| Region | Lake Macquarie, Newcastle |
| Ethnicity | Awabakal, Geawegal, Wonnarua |
| Extinct | Sometime late in the 19th century. The language is currently in early stages of revival. |
| Language family | |
| Dialects |
Awabagal
Geawegal
Wonarua
|
| AIATSIS | S66 |
Awabakal (also Awabagal or the Hunter River – Lake Macquarie, often abbreviated HRLM ) language is an Australian Aboriginal language that was spoken around Lake Macquarie and Newcastle in New South Wales. The name is derived from Awaba, which was the native name of the lake. It was spoken by Awabakal and Wonnarua peoples.
It was studied by missionary Lancelot Threlkeld in the 19th century, who wrote a grammar of the language, but the spoken language had died out before 21st-century revival efforts.
Contents
Classification
Awabakal is a Pama–Nyungan language, most closely related to the Worimi language, within the Yuin–Kuric group of Pama–Nyungan.
History
Awabakal was studied by the Reverend Lancelot Threlkeld from 1825 until his death in 1859, producing a grammar and dictionary in An Australian Grammar in 1834. The speaker of Awabakal who taught him about the language was Biraban, the tribal leader. Threlkeld and Biraban's Specimens of a Dialect of the Aborigines of New South Wales in 1827 was the earliest attempt at exhibiting the structure of an Australian language.
Threlkeld's work was greatly expanded by John Fraser and republished in 1892 as An Australian language as spoken by the Awabakal, the people of Awaba or Lake Macquarie (near Newcastle, New South Wales) being an account of their language, traditions and customs / by L.E. Threlkeld; re-arranged, condensed and edited with an appendix by John Fraser. It contained a grammar and vocabulary as well as much new material by Fraser, and helped to popularise the name "Awabakal" for the language grouping more broadly referred to as the Hunter River-Lake Macquarie language.
Modern revival
The language is currently being revived. A new orthography and reconstruction of the phonology has been undertaken. To date, several publications have been produced including "A grammar for the Awabakal language", "An introduction to the Awabakal language : its orthography, recommended orthoepy and its grammar and stylistics " and "Nupaleyalaan palii Awabakalkoba = Teach yourself Awabakal".
Phonology
Awabakal ceased to be a spoken language since long before the creation of recording equipment, and part of the revival process has been the reconstruction of the phonology. Therefore, the exactness of the language's sounds will never be historically precise. This process has, however, produced one which will be satisfactory for the purpose of revitalisation.
Vowels
| a – similar to English cut | /a/ |
| aa – long father | /aː/ |
| ai – eye | /aɪ/ |
| au – cut and bull together quickly. Similar to Scottish English "cow" | /aʊ/ |
| e – air but short | /æ~e/ |
| ei – way | /eɪ/ |
| i – pit | /i/ |
| ii – need | /iː/ |
| o – or but shorter | /œ/ |
| oo – or but longer | /œː/ |
| u – food but shorter | /u/ |
Consonants
| b,p – closer to English p than b – The lips are tense. | [p͈] – labio-tensive |
| k – Like English k but further back | [q] |
| l – value | [l̻] – laminal, possible palatised in some situations |
| m – like English m | [m͈] – labio-tensive |
| n – something like onion | [n̻] ~ [n̺] – laminal when beginning a syllable, apical when word final |
| ng – sing, ring | [ŋ] – possibly further back, [ɴ], like the k |
| r – trilled or rolled r | [r] |
| t – something like tune in Australian English | [t̻] – laminal stop, slightly aspirated, sometimes similar to an affricate |
| w – like English w, lips not as close together | [β̞] |
| y – like English y, tongue not as close to the top palate | [j] – but the tongue is mid-centralised |
Grammar
Nouns
There exist three noun classes. The first has 4 declension patterns. A noun can exist in any of 13 cases.
1st class – Common nouns, descriptors, demonstratives and minaring ('what?'). 2nd class – Place names, words of spatial relations and wonta ('where?'). 3rd class – Persons' names, kinship terms and ngaan ('who?').
The default, unmarked case of nouns is the absolutive. Unlike English and many European languages, in which an unmarked noun is the nominative case, and is (in the active voice) the subject of the sentence, Awabakal merely references a particular noun with this case.
Descriptors
There is a category of words in Awabakal called descriptors. They can stand as referring terms and are in these cases similar to nouns, like adjectives or intransitive verbs/predicative verb-adjective phrases. They can be declined into nominal cases.
Numbers
There are four number words.
- Wakool – one
- Bulowara – two
- Ngoro – three
- Wara – four or five (also the word for the palm of the hand → a handful of)
Pronominal enclitics
Pronominal enclitics are suffixes which have several functions and can be attached to verbs, descriptors, appositions, interrogatives, negatives and nouns. The numbers are: singular, dual and plural with a feminine/masculine distinction in the first person. They mark verbs for person, number, case and voice. The "ergative" enclitcs imply an active transitive situation and the "accusative" implies a passive intransitive situation. There are three true pronouns which could be called a nominative or topic case. There are only found at the beginning of an independent clause. These pronominals are found in ergative, accusative, dative and possessive cases.
Demonstratives
There are 3 degrees. They are declined for 10 cases.
- 'this' near the speaker
- 'that' near the addressee(s)
- 'that' there (but at hand)
Appositive demonstratives
Here too, there are 3 degrees. These terms indicate place. They decline for 13 cases.
Verbs
The default verbative voice of Awabakal verbs is neutral. I.e. they do not give a sense of active or passive. The pronominal enclitics indicate which voice the verb should be analysed as being in. There are 3 present tenses, 8 future and 7 past, with various voice, aspect and mood modifications.
Example:
kariwang+ku
magpie+ERG
minaring
what(ABS)
ta+taan?
eat+PRES
'What does the magpie eat?'
minaring+ku
what+ERG
kariwang
magpie(ABS)
ta+taan
eat+PRES
'What eats the magpie?'
Negatives
There are 10 forms of negatives which work with different types of words or phrases.
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are not commonly used in comparison to many languages. Sentences can often be connected without their use. These also have various combinations and case declinations.
Interrogatives
- Ngaan – who?
- Minaring – what?
- Wonta – where?
- Yakowai – how?
- Yakowanta – when?
- Korakowa – why not?
- Wiya – say (how about) ...
Examples
- Wonto ba kauwȧllo mankulla unnoa tara túġunbilliko ġurránto ġéen kinba,
- 2. Yanti bo ġearun kin bara ġukulla, unnoa tara nakillikan kurri-kurri kabiruġ ġatun mankillikan wiyellikanne koba.
- 3. Murrȧrȧġ tia kȧtan yantibo, koito baġ ba tuiġ ko ġirouġ Teopolo murrȧrȧġ ta,
- 4. Gurra-uwil koa bi tuloa, unnoa tara wiyatoara banuġ ba.
- —Introduction of the Gospel of Luke
The Lord's Prayer
Below is the Lord's Prayer in Awabakal, according to the Gospel of Luke. Part of the Gospel of Luke was translated into Awabakal in 1892 and below the text reflects the orthography of the prayer in 1892.
Ġatun noa wiya barun, wiyånůn ba,
ġiakai wiyånůn nura,
Biyuġbai ġearúmba wokka ka ba moroko ka ba kåtan, Kåmůnbilla yitirra ġiroúmba.
Ġurrabunbilla wiyellikanne ġiroúmba,
yanti moroko ka ba, yanti ta purrai ta ba.
Ġuwoa ġearún purreåġ ka takilliko.
Ġatun warekilla ġearúnba yarakai umatoara,
kulla ġéen yanti ta wareka yanti ta wiyapaiyeůn ġearúnba.
Ġatun yuti yikpra ġearún yarakai umullikan kolaġ;
mitomulla ġearún yarakai tabiruġ.
Influence on English
The word Koori, a self-referential term used by some Aboriginal people, comes from Awabakal.
See also
 In Spanish: Idioma awabakal para niños
In Spanish: Idioma awabakal para niños