Anubis facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Anubis |
|
|---|---|
The Egyptian god Anubis (a modern rendition inspired by New Kingdom tomb paintings)
|
|
| Major cult center | Lycopolis, Cynopolis |
| Symbol | Mummy gauze, jackal, flail |
| Personal information | |
| Consort | Anput, Nephthys |
| Offspring | Kebechet |
| Parents | Nepthys and Set, Osiris (Middle and New kingdom), or Ra (Old kingdom). |
| Siblings | Wepwawet |
| Greek equivalent | Hades or Hermes |
Anubis ( Ancient Greek: Ἄνουβις), also known as Inpu, Inpw, Jnpw, or Anpu in Ancient Egyptian (Coptic: ⲁⲛⲟⲩⲡ, romanized: Anoup) is the god of funerary rites, protector of graves, and guide to the underworld, in ancient Egyptian religion, usually depicted as a canine or a man with a dog's head.
Anubis was also an embalmer. By the Middle Kingdom (c. 2055–1650 BC) he was replaced by Osiris in his role as lord of the underworld. One of his prominent roles was as a god who ushered souls into the afterlife. He attended the weighing scale during the "Weighing of the Heart", in which it was determined whether a soul would be allowed to enter the realm of the dead. Anubis is one of the most frequently depicted and mentioned gods in the Egyptian pantheon.
Anubis was depicted in black, a color that symbolized regeneration, life, the soil of the Nile River, and the discoloration of the corpse after embalming. Anubis is associated with his brother Wepwawet, another Egyptian god portrayed with a dog's head or in canine form, but with grey or white fur. Historians assume that the two figures were eventually combined. Anubis' female counterpart is Anput. His daughter is the serpent goddess Kebechet.
Contents
Name

"Anubis" is a Greek rendering of this god's Egyptian name. Before the Greeks arrived in Egypt, around the 7th century BC, the god was known as Anpu or Inpu. The root of the name in ancient Egyptian language means "a royal child."
Inpu has a root to "inp", which means "to decay." The god was also known as:
- "First of the Westerners,"
- "Lord of the Sacred Land,"
- "He Who is Upon his Sacred Mountain,"
- "Ruler of the Nine Bows,"
- "The Dog who Swallows Millions,"
- "Master of Secrets,"
- "He Who is in the Place of Embalming," and
- "Foremost of the Divine Booth."
Anubis' name jnpw was possibly pronounced [a.ˈna.pʰa(w)].
History
In Egypt's Early Dynastic period (c. 3100 – c. 2686 BC), Anubis was portrayed in full animal form, with a "jackal" head and body.
In Predynastic Egypt the dead were buried in shallow graves, so jackals had been strongly associated with cemeteries because they were scavengers feeding on corpses.
In the Old Kingdom, Anubis was the most important god of the dead. He was replaced in that role by Osiris during the Middle Kingdom (2000–1700 BC). In the Roman era, which started in 30 BC, tomb paintings depict him holding the hand of deceased persons to guide them to Osiris.
In early mythology, he was portrayed as a son of Ra. Around 2181–2055 BC, Anubis was the son of either the cow goddess Hesat or the cat-headed Bastet. Another tradition depicted him as the son of Ra and Nephthys. The Greek Plutarch (c. 40–120 AD) reported a tradition that Anubis was the illegitimate son of Nephthys and Osiris, but that he was adopted by Osiris's wife Isis:
In Nubia, Anubis was seen as the husband of his mother Nephthys.
Roles
Embalmer
Anubis was associated with mummification. He was also called ḫnty zḥ-nṯr "He who presides over the god's booth", in which "booth" could refer either to the place where embalming was carried out or the pharaoh's burial chamber.
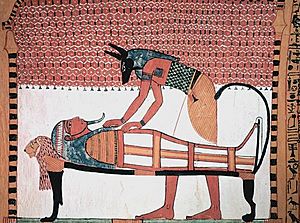
In the Osiris myth, Anubis helped Isis to embalm Osiris. Indeed, when the Osiris myth emerged, it was said that after Osiris had been killed by Set, Osiris's organs were given to Anubis as a gift. With this connection, Anubis became the patron god of embalmers; during the rites of mummification, illustrations from the Book of the Dead often show a wolf-mask-wearing priest supporting the upright mummy.
Protector of tombs
Anubis was a protector of graves and cemeteries.
The Jumilhac papyrus recounts another tale where Anubis protected the body of Osiris from Set. Set attempted to attack the body of Osiris by transforming himself into a leopard. Anubis stopped Set, however, and he branded Set's skin with a hot iron rod. Anubis then wore Set's skin as a warning against evil-doers who would desecrate the tombs of the dead. Priests who attended to the dead wore leopard skin in order to commemorate Anubis' victory over Set. The legend of Anubis branding the hide of Set in leopard form was used to explain how the leopard got its spots.
Most ancient tombs had prayers to Anubis carved on them.
Guide of souls
By the late pharaonic era (664–332 BC), Anubis was often depicted as guiding individuals across the threshold from the world of the living to the afterlife.
Weigher of hearts
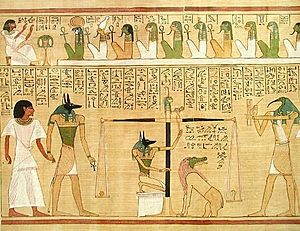
One of the roles of Anubis was as the "Guardian of the Scales." The critical scene depicting the weighing of the heart, in the Book of the Dead, shows Anubis performing a measurement that determined whether the person was worthy of entering the realm of the dead (the underworld, known as Duat). By weighing the heart of a deceased person against Ma'at (or "truth"), who was often represented as an ostrich feather, Anubis dictated the fate of souls. Souls heavier than a feather would be devoured by Ammit, and souls lighter than a feather would ascend to a heavenly existence.
Portrayal in art
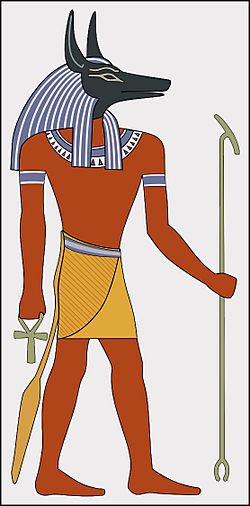
Anubis was one of the most frequently represented deities in ancient Egyptian art. He is depicted in royal tombs as early as the First Dynasty. The god is typically treating a king's corpse, providing sovereign to mummification rituals and funerals, or standing with fellow gods at the Weighing of the Heart of the Soul in the Hall of Two Truths. One of his most popular representations is of him, with the body of a man and the head of a jackal with pointed ears, standing or kneeling, holding a gold scale while a heart of the soul is being weighed against Ma'at's white truth feather.
In the early dynastic period, he was depicted in animal form, as a black canine. Anubis's distinctive black color did not represent the animal, rather it had several symbolic meanings. It represented "the discolouration of the corpse after its treatment with natron and the smearing of the wrappings with a resinous substance during mummification." Being the color of the fertile silt of the River Nile, to Egyptians, black also symbolized fertility and the possibility of rebirth in the afterlife. In the Middle Kingdom, Anubis was often portrayed as a man with the head of a jackal. An extremely rare depiction of him in fully human form was found in a chapel of Ramesses II in Abydos.
Anubis is often depicted wearing a ribbon and holding a nḫ3ḫ3 "flail" in the crook of his arm. Another of Anubis's attributes was the jmy-wt or imiut fetish, named for his role in embalming. In funerary contexts, Anubis is shown either attending to a deceased person's mummy or sitting atop a tomb protecting it. New Kingdom tomb-seals also depict Anubis sitting atop the nine bows that symbolize his domination over the enemies of Egypt.
-
Lintel of Amenemhat I and deities; 1981–1952 BC; painted limestone; 36.8 × 172 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art (New York City)
-
The Anubis Shrine; 1336–1327 BC; painted wood and gold; 1.1 × 2.7 × 0.52 m; from the Valley of the Kings; Egyptian Museum (Cairo)
Worship
Although he does not appear in many myths, he was extremely popular with Egyptians and those of other cultures. The Greeks linked him to their god Hermes, the god who guided the dead to the afterlife. The pairing was later known as Hermanubis. Anubis was heavily worshipped because, despite modern beliefs, he gave the people hope. People marveled in the guarantee that their body would be respected at death, their soul would be protected and justly judged.
Anubis had male priests who sported wood masks with the god's likeness when performing rituals. His cult center was at Cynopolis in Upper Egypt but memorials were built everywhere and he was universally revered in every part of the nation.
In popular culture
In popular and media culture, Anubis is often falsely portrayed as the sinister god of the dead. He gained popularity during the 20th and 21st centuries through books, video games, and movies where artists would give him evil powers and a dangerous army. Despite his nefarious reputation, his image is still the most recognizable of the Egyptian gods and replicas of his statues and paintings remain popular.
See also
 In Spanish: Anubis para niños
In Spanish: Anubis para niños