Ananke (moon) facts for kids
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | S. B. Nicholson |
| Discovery date | September 28, 1951 |
| Orbital characteristics | |
| Periapsis | 12,567,000 km |
| Apoapsis | 29,063,500 km |
|
Mean orbit radius
|
21,280,000 km |
| Eccentricity | 0.24 |
| 610.45 d (1.680 a) | |
|
Average orbital speed
|
2.367 km/s |
| Inclination | 148.89° (to the ecliptic) 149.9° (to Jupiter's equator) |
| Satellite of | Jupiter |
| Physical characteristics | |
|
Mean radius
|
14 km |
| ~2500 km2 | |
| Volume | ~11,500 km3 |
| Mass | 4.0×1016 kg |
|
Mean density
|
2.6 g/cm3 (assumed) |
| 0.010 m/s2 (0.001 g) | |
| ~0.017 km/s | |
| Albedo | 0.04 (assumed) |
| Temperature | ~124 K |
Ananke is a retrograde non-spherical moon of Jupiter. It was found by Seth Barnes Nicholson at Mount Wilson Observatory in 1951 and is named after the mythological Ananke, the mother of Adrastea by Jupiter. The adjectival form of the name is Anankean.
Ananke did not get its present name until 1975; before then, it was simply known as Jupiter XII. It was sometimes called "Adrastea" between 1955 and 1975. Note that Adrastea is now the name of another moon of Jupiter.
Ananke gives its name to the Ananke group, retrograde non-spherical moons which orbit Jupiter between 19,300,000 and 22,700,000 km, at inclinations of about 150°.
Orbit
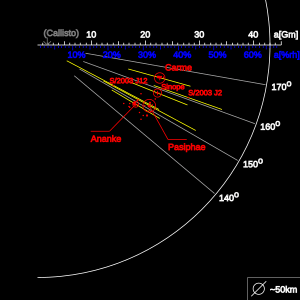
Ananke orbits Jupiter on a high eccentricity and high inclination retrograde orbit. Eight non-spherical moons found since 2000 follow similar orbits. The orbital elements are as of January 2000. They are changing a lot due to Solar and planetary perturbations. The diagram illustrates Ananke's orbit in relation to other retrograde non-spherical moons of Jupiter. The eccentricity of selected orbits is represented by the yellow segments (extending from the pericentre to the apocentre). The farthest spherical moon Callisto is located for reference.
Given these orbital elements and the physical characteristics known so far, Ananke is thought to be the biggest remnant of an original break-up forming the Ananke group.
Physical characteristics
In the visible spectrum, Ananke appears grey to light-red.
The infrared spectrum is similar to P-type asteroids but with a possible indication of water.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Ananké (satélite) para niños
In Spanish: Ananké (satélite) para niños