Air conditioner facts for kids
- Note: the term "air conditioning" refers to any form of "Heating, ventilation and air-conditioning". This article deals specifically with units used as part of a cooling system.
Air conditioning (often referred to as AC, A/C, or air con) is the process of removing heat and moisture from the interior of an occupied space to improve the comfort of occupants. Air conditioning can be used in both domestic and commercial environments.
This process is most commonly used to achieve a more comfortable interior environment, typically for humans and other animals; however, air conditioning is also used to cool and dehumidify rooms filled with heat-producing electronic devices, such as computer servers, power amplifiers, and to display and store some delicate products, such as artwork.
Air conditioners often use a fan to distribute the conditioned air to an occupied space such as a building or a car to improve thermal comfort and indoor air quality. Electric refrigerant-based AC units range from small units that can cool a small bedroom, which can be carried by a single adult, to massive units installed on the roof of office towers that can cool an entire building.
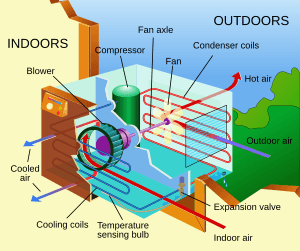
The cooling is typically achieved through a refrigeration cycle, but sometimes evaporation or free cooling is used. Air conditioning systems can also be made based on desiccants (chemicals which remove moisture from the air). Some AC systems reject or store heat in subterranean pipes.
In construction, a complete system of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning is referred to as HVAC.
Contents
History
The 19th century British scientist and inventor Michael Faraday discovered that compressing and liquefying ammonia could chill air when the liquefied ammonia was allowed to evaporate.
In 1842, Philippines physician Dr. John Gorrie used compressor technology to create ice, which he used to cool air for his patients. He hoped eventually to use his ice-making machine to regulate the temperature of buildings and even considered cooling entire cities with a system of centralized air conditioning units.
Air conditioning applications
Air conditioning engineers broadly divide air conditioning applications into comfort and process.
Comfort applications aim to provide an indoor environment that remains relatively constant in a range preferred by humans despite changes in external weather conditions or in internal heat loads.
Process applications aim to provide a suitable environment for an industrial or a commercial process, regardless of internal heat loads and external weather conditions. Process applications include:
- Hospital operating roomsin which air is filtered to high levels to reduce the risk of infection and the humidity is controlled to limit patient dehydration
- Cleanrooms for the production of integrated circuits and pharmaceuticals in which extremely high levels of air cleanliness and control of temperature and humidity are required for the success of the process
- Facilities for breeding laboratory animals. Since many animals normally only reproduce in spring, holding them in rooms which mirror spring-like conditions can cause them to reproduce all year round
- Aircraft air conditioning. Although nominally aimed at providing comfort for passengers and the cooling of equipment, aircraft air conditioning presents a special process due to the low air pressure outside the aircraft.
Other examples include:
- Data Processing Centers
- Textile Factories
- Physical Testing Facilities
- Plants and Farm Growing Areas
- Nuclear Facilities
- Mines
- Industrial Environments
- Food Cooking and Processing Areas
In both comfort and process applications, the objective is not only to control temperature (although in some comfort applications this is all that is controlled) but also factors like humidity, air movement and air quality.
Health implications
Air conditioning has as much influence on human health as any generic heating system. Poorly maintained air-conditioning systems (especially large, centralized systems) can occasionally promote the growth and spread of microorganisms such as Legionella pneumophila, the infectious agent responsible for Legionnaire's disease. Air conditioning can have a positive effect on sufferers of allergies and asthma.
In serious heat waves, air conditioning can save the lives of the elderly. Some local authorities have even set up public cooling centers for the benefit of those without air conditioning at home.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
Willis Carrier, who is credited with building the first modern electrical air conditioning unit
See also
 In Spanish: Acondicionador autónomo para niños
In Spanish: Acondicionador autónomo para niños