Abscess facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Abscess |
|
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Latin: Abscessus |
 |
|
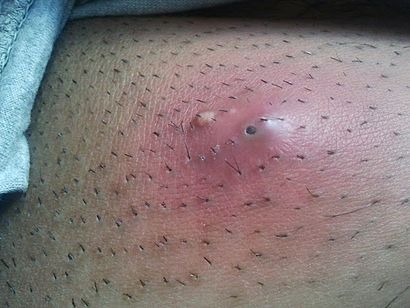
| Five-day-old inflamed epidermal inclusion cyst. The black spot is a keratin plug which connects with the underlying cyst. | |
| Symptoms | Redness, pain, swelling |
| Usual onset | Rapid |
| Causes | Bacteria (often MRSA) |
| Diagnostic method | Ultrasound, CT scan |
| Similar conditions | Cellulitis, sebaceous cyst, necrotising fasciitis |
| Treatment | Cutting it open |
| Frequency | ~1% per year (United States) |
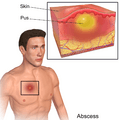
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger.
They are usually caused by a bacterial infection. Often many different types of bacteria are involved in a single infection. In the United States and many other areas of the world the most common bacteria present is methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Rarely, parasites can cause abscesses; this is more common in the developing world.
Diagnosis of a skin abscess is usually made based on what it looks like and is confirmed by cutting it open. Ultrasound imaging may be useful in cases in which the diagnosis is not clear.
Standard treatment for most skin or soft tissue abscesses is cutting it open and drainage. There appears to be some benefit from also using antibiotics. A small amount of evidence supports not packing the cavity that remains with gauze after drainage.
Closing this cavity right after draining it rather than leaving it open may speed healing without increasing the risk of the abscess returning.
Skin abscesses are common and have become more common in recent years.
In 2005 in the United States, 3.2 million people went to the emergency department for an abscess. In Australia, around 13,000 people were hospitalized in 2008 with the condition.
Signs and symptoms
Abscesses may occur in any kind of tissue but most frequently on skin surface (where they may be superficial pustules (boils) or deep skin abscesses), in the lungs, brain, teeth, kidneys, and tonsils. Major complications are spreading of the abscess material to adjacent or remote tissues, and extensive regional tissue death (gangrene).
An internal abscess is more difficult to identify, but signs include pain in the affected area, a high temperature, and generally feeling unwell. Internal abscesses rarely heal themselves, so prompt medical attention is indicated if such an abscess is suspected. An abscess can potentially be fatal depending on where it is located.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Absceso para niños
In Spanish: Absceso para niños