ATLAS experiment facts for kids

ATLAS (A Toroidal LHC ApparatuS) is the biggest experiment at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC).
It is one of the seven particle detector experiments (ALICE, ATLAS, CMS, TOTEM, LHCb, and LHCf) built at the LHC. LHC is a new particle accelerator at the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN) in Switzerland. ATLAS is 46 metres long and 25 metres in diameter, weighing about 7,000 tonnes. The project is led by Fabiola Gianotti. The project has 2,000 scientists and engineers at 165 institutions in 35 countries. The project began operation on 10 September 2008. ATLAS studies highly massive particles which could not be studied using earlier lower-energy accelerators. ATLAS may start new theories of particle physics beyond the Standard Model.
Images for kids
-
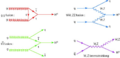
Schematics, called Feynman diagrams show the main ways that the Standard Model Higgs boson can be produced from colliding protons at the LHC.
-
The TRT (Transition Radiation Tracker) central section, the outermost part of the Inner Detector, assembled above ground and taking data from cosmic rays in September 2005.
-
September 2005: The main barrel section of the ATLAS hadronic calorimeter, waiting to be moved inside the toroid magnets.
See also
 In Spanish: Experimento ATLAS para niños
In Spanish: Experimento ATLAS para niños