ARA General Belgrano facts for kids

ARA General Belgrano underway
|
|
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | USS Phoenix (CL-46) |
| Acquired | 3 October 1938 |
| Fate | Decommissioned 3 July 1946; Stricken 27 January 1951 |
| History | |
| Name | 17 de Octubre |
| Namesake | 17 October 1945, the day popular demonstrations forced the release of Juan Perón |
| Acquired | 9 April 1951 |
| Renamed | ARA General Belgrano (C-4) |
| Namesake | Manuel Belgrano |
| Fate | Torpedoed and sunk on 2 May 1982 |
| Badge |  |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Brooklyn-class light cruiser |
| Displacement | 9,575 tons (empty) 12,242 (full load) |
| Length | 608.3 ft (185.4 m) |
| Beam | 61.8 ft (18.8 m) |
| Draft | 19.5 ft (5.9 m) |
| Speed | 32.5 knots (60.2 km/h; 37.4 mph) |
| Complement | 1,138 officers and men |
| Armament |
|
| Armor |
|
| Aircraft carried | 2 helicopters (One Aérospatiale Alouette III was on board when sunk) |
ARA General Belgrano (C-4) was an Argentine Navy light cruiser in service from 1951 until 1982. Originally commissioned by the U.S. Navy as USS Phoenix, she saw action in the Pacific theatre of World War II before being sold to Argentina. The vessel was the second to have been named after the Argentine founding father Manuel Belgrano (1770–1820). The first vessel was a 7,069-ton armoured cruiser completed in 1896.
She was sunk on 2 May 1982 during the Falklands War by the Royal Navy submarine Conqueror with the loss of 323 lives. Losses from General Belgrano totalled just under half of Argentine military deaths in the war.
She is the only ship to have been sunk during military operations by a nuclear-powered submarine and the second sunk in action by any type of submarine since World War II (the first being the Indian frigate INS Khukri, which was sunk by the Pakistani submarine PNS Hangor during the 1971 Indo-Pakistani War).
Contents
Early career

The warship was built as USS Phoenix, the sixth ship of the Brooklyn-class cruiser design, in Camden, New Jersey, by the New York Shipbuilding Corporation starting in 1935, and launched in March 1938. She survived the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor in 1941 undamaged, and went on to earn nine battle stars for World War II service. At the end of the war, she was placed in reserve at Philadelphia on 28 February 1946, decommissioned on 3 July that year and remained laid up at Philadelphia.
Phoenix was sold to Argentina in October 1951 and renamed 17 de Octubre after the "People's Loyalty day", an important symbol for the political party of the then-president Juan Perón. Sold with her was another of her class, the USS Boise, renamed ARA Nueve de Julio, which was withdrawn in 1977.
17 de Octubre was one of the main naval units that joined the 1955 coup in which Perón was overthrown, and was renamed General Belgrano after Manuel Belgrano, a lawyer who had founded the Escuela de Náutica (School of Navigation) in 1799 and with the rank of general fought for Argentine independence from 1811 to 1819. General Belgrano accidentally rammed her sister ship Nueve de Julio on exercises in 1956, which resulted in damage to both. General Belgrano was outfitted with the Sea Cat anti-aircraft missile system between 1967 and 1968.
Sinking
On 12 April 1982, following the 1982 invasion of the Falkland Islands, Britain declared a 200-nautical-mile (370 km) Maritime Exclusion Zone (MEZ) around the Falkland Islands within which any Argentine warship or naval auxiliary entering the MEZ might be attacked by British nuclear-powered submarines (SSN). On 23 April, the British Government clarified in a message that was passed via the Swiss Embassy in Buenos Aires to the Argentine government that any Argentine ship or aircraft that was considered to pose a threat to British forces would be attacked.
On 30 April this was upgraded to the total exclusion zone, within which any sea vessel or aircraft from any country entering the zone might be fired upon without further warning. The zone was stated to be "...without prejudice to the right of the United Kingdom to take whatever additional measures may be needed in exercise of its right of self-defence, under Article 51 of the United Nations Charter." The concept of a total exclusion zone was a novelty in maritime law; the Law of the Sea Convention had no provision for such an instrument. Its purpose seems to have been to increase the amount of time available to ascertain whether any vessel in the zone was hostile or not. Regardless of the uncertainty of the zone's legal status, it was widely respected by the shipping of neutral nations.
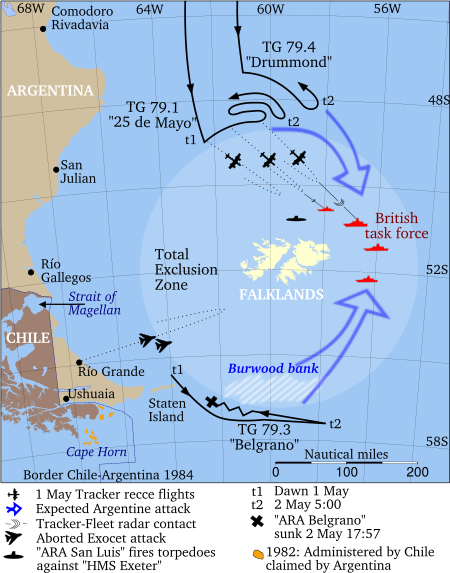
The Argentine military junta began to reinforce the islands in late April when it was realised that the British Task Force was heading south. As part of these movements, Argentine naval units were ordered to take positions around the islands. Two Task Groups designated 79.1, which included the aircraft carrier ARA Veinticinco de Mayo plus two Type 42 destroyers, and 79.2, which included three Exocet missile armed Drummond-class corvettes, both sailed to the north. General Belgrano had left Ushuaia in Tierra del Fuego on 26 April. Two destroyers, ARA Piedra Buena and ARA Hipólito Bouchard (also ex-USN vessels) were detached from Task Group 79.2 and together with the tanker YPF Puerto Rosales, joined General Belgrano to form Task Group 79.3.
By 29 April, the ships were patrolling the Burdwood Bank, south of the islands. On 30 April, General Belgrano was detected by the British nuclear-powered hunter-killer submarine Conqueror. The submarine approached over the following day. On 1 May 1982, Admiral Juan Lombardo ordered all Argentine naval units to seek out the British task force around the Falklands and launch a "massive attack" the following day. General Belgrano, which was outside and to the south-west of the exclusion zone, was ordered south-east.
Lombardo's signal was intercepted by British Intelligence. As a result, Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher and her War Cabinet, meeting at Chequers the following day, agreed to a request from Admiral Terence Lewin, the Chief of the Defence Staff, to alter the rules of engagement and allow an attack on General Belgrano outside the exclusion zone. Although the group was outside the British-declared total exclusion zone of 370 km (200 nautical miles) radius from the islands, the British decided that it was a threat. After consultation at Cabinet level, Thatcher agreed that Commander Chris Wreford-Brown should attack General Belgrano.
At 14:57 (Falkland Islands Time) on 2 May, Conqueror fired three 21-inch Mk 8 mod 4 torpedoes (conventional, non-guided, torpedoes), each with an 805-pound (363 kg) Torpex warhead. While Conqueror was also equipped with the newer Mark 24 Tigerfish homing torpedo, there were doubts about its reliability. Initial reports from Argentina claimed that Conqueror fired two Tigerfish torpedoes on General Belgrano. Two of the three torpedoes hit General Belgrano. According to the Argentine government, General Belgrano's position was 55°24′S 61°32′W / 55.400°S 61.533°W.
One of the torpedoes struck 10 to 15 metres (33 to 49 ft) aft of the bow, outside the area protected by either the ship's side armour or the internal anti-torpedo bulge. This blew off the ship's bow, but the internal torpedo bulkheads held and the forward powder magazine for the 40 mm gun did not detonate. It is believed that none of the ship's company were in that part of the ship at the time of the explosion.
The second torpedo struck about three-quarters of the way along the ship, just outside the rear limit of the side armour plating. The torpedo punched through the side of the ship before exploding in the aft machine room. The explosion tore upward through two messes and a relaxation area called "the Soda Fountain" before finally ripping a 20-metre-long (66 ft) hole in the main deck. Later reports put the number of deaths in the area around the explosion at 275 men. After the explosion, the ship rapidly filled with smoke. The explosion also damaged General Belgrano's electrical power system, preventing her from putting out a radio distress call. Though the forward bulkheads held, water was rushing in through the hole created by the second torpedo and could not be pumped out because of the electrical power failure. In addition, although the ship should have been "at action stations", she was sailing with the water-tight doors open.
The ship began to list to port and to sink towards the bow. Twenty minutes after the attack, at 16:24, Captain Bonzo ordered the crew to abandon ship. Inflatable life rafts were deployed, and the evacuation began without panic.
The two escort ships were unaware of what was happening to General Belgrano, as they were out of touch with her in the gloom and had not seen the distress rockets or lamp signals. Adding to the confusion, the crew of Bouchard felt an impact that was possibly the third torpedo striking at the end of its run (an examination of the ship later showed an impact mark consistent with a torpedo). The two ships continued on their course westward. By the time the ships realised that something had happened to General Belgrano, it was already dark and the weather had worsened, scattering the life rafts.
Argentine and Chilean ships rescued 772 men from 3 to 5 May. In total, 323 were killed in the attack: 321 members of the crew and two civilians who were on board at the time.
Following the loss of General Belgrano, the Argentine fleet returned to its bases and played no major role in the rest of the conflict. British nuclear submarines continued to operate in the sea areas between Argentina and the Falkland Islands, gathering intelligence, providing early warning of air raids and effectively imposing sea denial. A further effect was that the Argentinian Navy's carrier-borne aircraft had to operate from land bases at the limit of their range, rather than from an aircraft carrier at sea. The minimal role of the Navy in the rest of the campaign led to a considerable loss of credibility and influence within the Junta.
Aftermath
In August 1994, an official Argentine Defence Ministry report written by armed forces auditor Eugenio Miari was released which described the sinking of General Belgrano as "a legal act of war", explaining that "acts of war can be carried out in all of the enemy's territory" and "they can also take place in those areas over which no state can claim sovereignty, in international waters". Argentinian veterans were said to be dismayed at the conclusion about General Belgrano and the President of the Federation of Argentine War Veterans Luis Ibáñez hoped to produce more witnesses to show that the sinking was a war crime.
In 1999 Sir Michael Boyce, First Sea Lord of the Royal Navy, visited the Puerto Belgrano naval base and paid tribute to those who died. In 2003 a search team aboard Seacor Lenga, crewed by Argentine and British veterans, was sponsored by National Geographic to find the sunken cruiser but failed to locate the ship. The area where General Belgrano sank, that was not found, is classified as a War Grave under Argentine Congress Law 25.546.
In 2000, lawyers representing the families of the sailors killed onboard General Belgrano attempted to sue the British Government in the European Court of Human Rights on the grounds that the attack took place outside the exclusion zone. It was an attempt to pressure the Argentine government to lodge an action against the UK in the International Court of Justice, but was ruled inadmissible by the Court of Human Rights on the grounds that it had been submitted too late.
La Nación published a reader's letter from Admiral Enrique Molina Pico (head of the Argentine Navy in the 1990s) in 2005 in which Molina Pico wrote that General Belgrano was part of an operation that posed a real threat to the British task force, but was holding off for tactical reasons. Molina Pico added that "To leave the exclusion zone was not to leave the combat zone to enter a protected area". Molina Pico explicitly stated that the sinking was not a war crime, but a combat action.
General Belgrano's captain, Héctor Bonzo, died on 22 April 2009, aged 76. He had spent his last years working for an association called Amigos del Crucero General Belgrano (Friends of the Cruiser General Belgrano) whose purpose was to help those affected by the sinking. Captain Bonzo also wrote his memories about the sinking in the book 1093 Tripulantes del Crucero ARA General Belgrano, published in 1992. In this book he wrote that it is "improper to accept that (...) the attack by HMS Conqueror was a betrayal". During an interview in 2003 he had stated that General Belgrano was only temporarily sailing to the west at the time of the attack, and his orders were to attack any British ships which came within range of the cruiser's armament.
In late 2011, Major David Thorp, a former British military intelligence officer who led the signals intercept team aboard HMS Intrepid, released the book The Silent Listener detailing the role of intelligence in the Falklands War. In the book he stated that despite the fact that General Belgrano was observed by Conqueror sailing away from the Falklands at the time of the attack, she had actually been ordered to proceed to a rendezvous point within the Exclusion Zone. A report prepared by Thorp for Thatcher several months after the incident stated the destination of the vessel was not to her home port as the Argentine Junta stated; the report was not released because the Prime Minister did not want to compromise British signals intelligence capabilities.
In 2012 the President of Argentina, Cristina Fernández de Kirchner, referred to the sinking of General Belgrano as a "war crime". However, the Argentine Navy has held the view that the sinking was a legitimate act of war, a position that was asserted by the Argentine Navy before various courts in 1995, and by the vessel's Captain Hector Bonzo in 2003.
See also
- List of cruisers
- List of ships of the Argentine Navy
- List of ships sunk by submarines by death toll